1. Thread Class
- 자바 Thread의 꼭 알아야 할 주요 기능으로는 sleep, interrupt, join이 있습니다.
public class Thread implements Runnable {
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
public void interrupt() {
if (this != Thread.currentThread()) {
checkAccess();
// thread may be blocked in an I/O operation
synchronized (blockerLock) {
Interruptible b = blocker;
if (b != null) {
interrupt0(); // set interrupt status
b.interrupt(this);
return;
}
}
}
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
join(0);
}
// (. . .) 생략
}
2. sleep()
- Thread 대기, Thread 재우기
- Thread를 재울 경우 다른 스레드에게 먼저 리소스 우선권이 전달됩니다.
- interrupt()를 이용하여 실행에 관여할 수 있습니다.(interrupt() 실행 시 InterruptedException 예외 발생)
- 관련 예외 : InterruptedException (자는 동안에 누군가가 이 스레드를 깨우면(예외를 일으키면) 그때 그 catch {}가 실행됩니다.)
Sleep() 예시 코드
// 람다로 스레드 만들기 (1. sleep)
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); // 1초 재우기
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread Test: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
thread1.start(); //스레드 실행
System.out.println("Main Test: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); // main 스레드
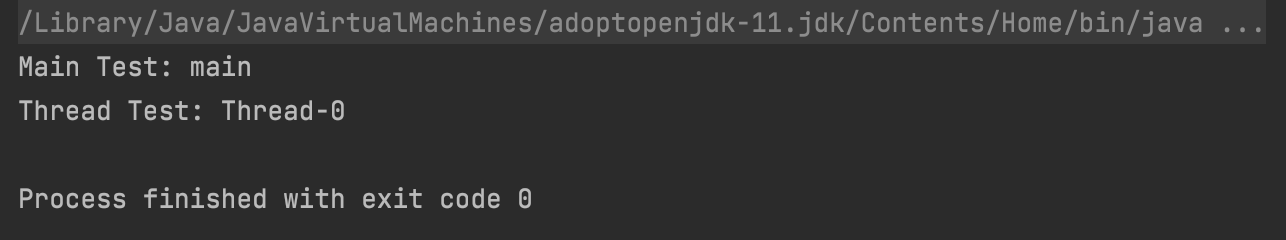
실행 결과
- thread1은 1초 대기 후 출력 작업을 시도하므로 main 스레드가 먼저 처리된 후에 처리가 됩니다.
3. interrupt()
- Thread를 깨우는 방법
- Thread 종류의 기능으로 사용하기도 합니다.
- InterruptedException를 활용하여 인터럽트 실행 시 처리 작업을 작성해줍니다.
interrupt() 예시
- 다음 예시의 thread2는 작업 실행(출력)후 1초 대기를 무한 반복하는 스레드입니다.
- 이 스레드를 종료하기 위해서는 InterruptedException 예외를 처리하는 코드를 작성하고 interrupt() 메소드를 실행해줘야 작업을 멈출 수 있습니다.
// (출력 -> 1초 대기)를 반복하는 무한 루프 스레드
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Thread Test: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("인터럽트 발생으로 종료합니다.");
return; // return void 인 경우 return은 종료를 의미합니다. (return을 안할경우 종료가 되지 않습니다.)
}
}
});
thread2.start();
System.out.println("Hello: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); // main 스레드
Thread.sleep(3000); // 3초 재우기
thread2.interrupt(); // 인터럽트 발생(종료)
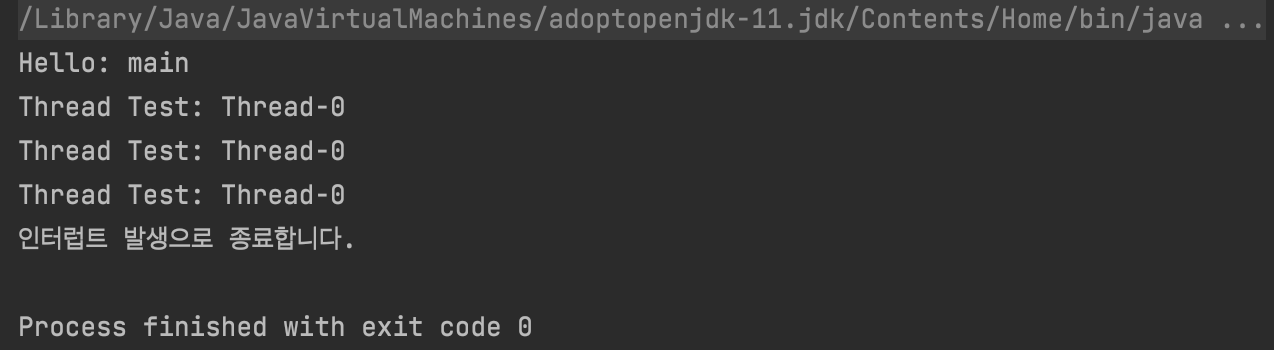
실행 결과
- thread2 출력 작업이 3번 실행된 후에 인터럽트 발생으로 인해 종료됩니다.
- 아래의 출력 결과는 main 스레드가 먼저 실행되었지만 항상 처음에 실행되지는 않습니다. (순서 보장 X)
4. join()
- join()을 실행한 Thread가 끝날 때까지 다른 Thread가 기다립니다.(작업이 종료될 때까지 기다려줍니다.)
- sleep()과 마찬가지로 interrupt()가 실행에 관여할 수 있습니다. (interrupt() 실행 시 InterruptedException 예외 발생)
- 아래의 예시는 main 스레드가 thread3을 기다리도록 구현했습니다.
join() 예시
// 3초 쉬고 끝나는 스레드
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("Thread Test: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
});
thread3.start();
System.out.println("Main 실행 시간: " + LocalDateTime.now()); // main 스레드
thread3.join(); // main 스레드가 thread3이 끝날때 까지 기다림(3초)
System.out.println("Main 종료 시간: " + LocalDateTime.now()); // 만약 위의 join으로 기다리지 않는 다면 이 출력문은 아무때나 출력이 됩니다.
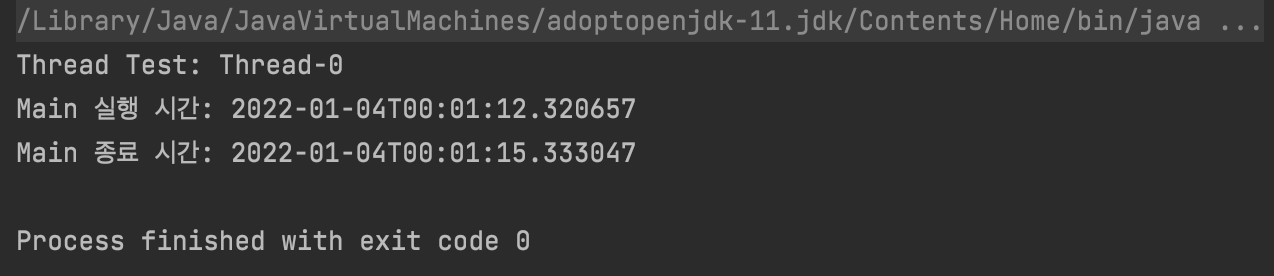
실행 결과
- 맨 마지막 main 스레드의 출력 작업이 thread3이 끝날 때 까지 기다렸다가 실행되는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
'Backend > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 자바 8 Stream API 루핑 (peek, forEach) (0) | 2022.01.07 |
|---|---|
| [Java] Executors Thread 사용법 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [Java] 자바 Thread 생성하기 (0) | 2022.01.04 |
| [Java] 자바 8 Stream API 필터링 (filter, distinct) (0) | 2022.01.01 |
| [Java] 자바 8 Stream API 소개 (java.util.stream) (0) | 2021.12.31 |
